TYPES
OF BUSINESS
A business is an
organisation that offers goods or services to customers, categorized
by economic sector, geographical area or size.
ECONOMIC SECTORS
Primary sector
business produce or extract raw natural materials (mining, forestry,
agriculture and fishing.
Secondary sector:
business process raw materials or use them. This is often done in
factories.
Tertiary sector:
businesses that offer a service (hairdressing, food services,
entertainment, tourism….)
SIZE
The size of the
business depends on the number of employees:
-
Micro-business:
1-9 employees
-
Small
business: 10-49 employees
-
Medium-sized
business: 50- 249 employees
-
Large
business: 250+ employees
GEOGRAPHICAL AREA
- A local business
operates in a small area (neighbourhood, town or city)
- A regional business
operates in a larger area (province, region)
- National business
does it in more tha one region of a country
- Multinational
business operates in more than one country or worldwide.
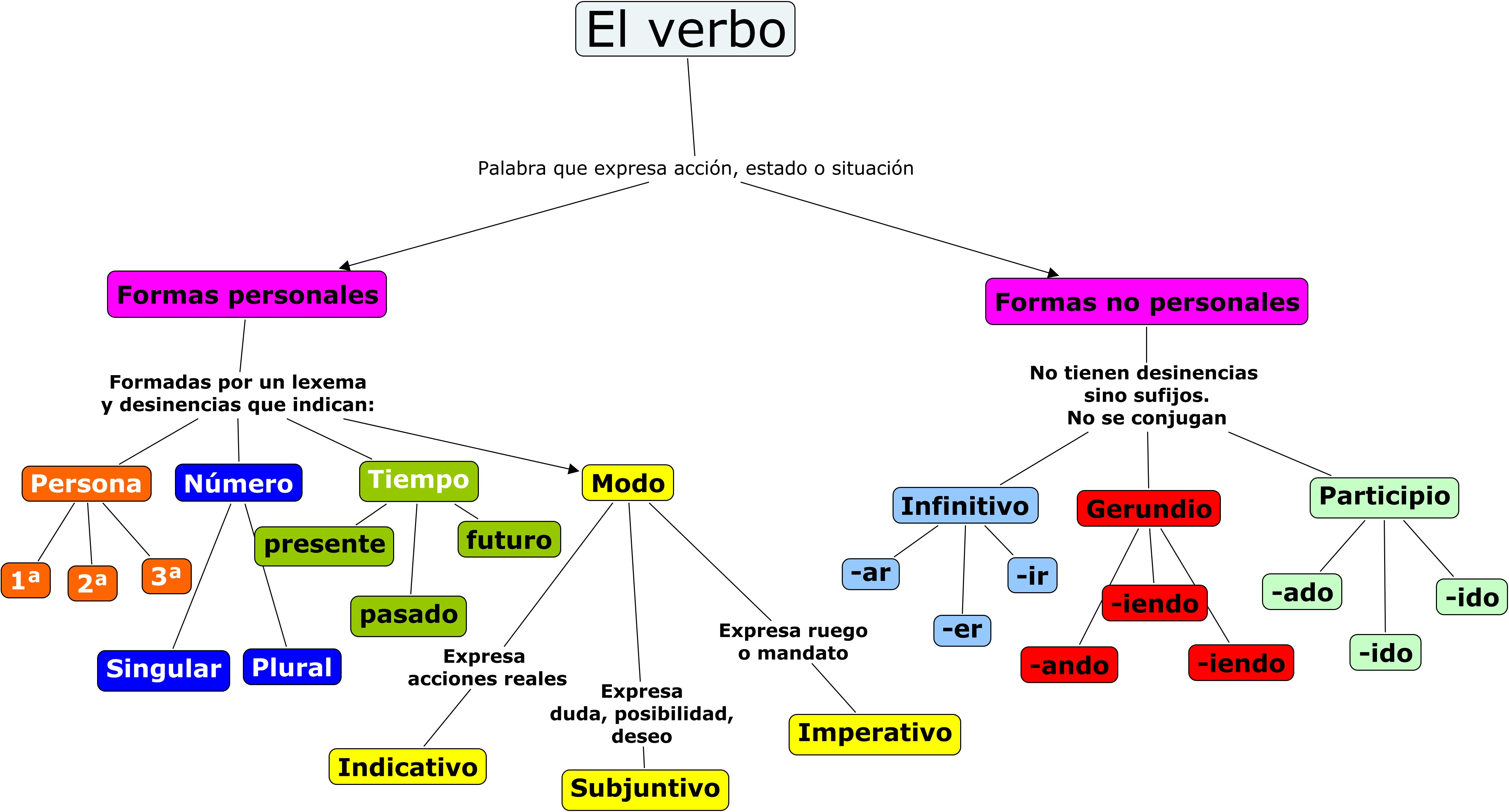
BUSINESS
ORGANISATION
Business organise
employees or staff into departments and levels: Organograms.
The Chief
Executive Officer(CEO) makes the most important decisions.
The directors
of the different depatments report to the CEO. In large business
there are financial director, sales director…
Managers
organise the daily activities of their departments and are
responsible for the team.
Supervisors:
report the managers.

Different
departments:
-
Production
department: responsible of how products are made
-
Marketing
department: responsible for advertising
-
Sales:
responsible for selling the services/products
-
Finance:
controls the money
-
Human
resources: hires and trains employees.
Small businesses do
not usually have as many levels of organisation, only teams and
supervisors, and the CEO is often the owner.
COSTS
OF RUNNING A BUSINESS
People who start
their own business are called entrepreneurs. Starting a
business has start-up costs. Some entrepreneurs get a loan
from a bank or a grant from the government.
The profit is
the extra money that a business has after it has paid all its running
costs (things paid day to day). They can be:
They need to be paid
on a regular basis. They include rent, salaries, utility services
such as telephone or internet and insurance in case of accident.
They depend on the
products and services that a business wants to sell. They change over
time.
Variable costs
include the materials a business needs to make its products. Shipping
costs cover the cost of delivering products to customers. Bonus
(extra money) if they meet sales or production objectives.
Promotional costs that depend on the type and amount of advertising.
SAVING
AND SPENDING MONEY
The movement of
money is calles cash flow. Money moves around when you earn
it, spend it or put it into investments or a bank account.
The bank uses the money or capital to do business and make a
profit, you receive it as interest.
SAVING MONEY
-
Keep a money
jar
-
Advantages:
quick and easy and you do not pay fees.
-
Disadvantages:
will not earn interest, money can get lost or stolen.
- Opening a
savings account
SPEND LESS AND SAVE
MORE
Shops often have
special offers and
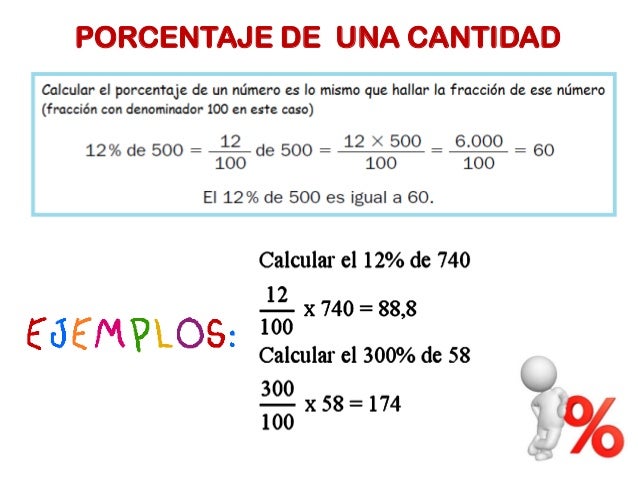
sales when prices are reduced. If you look at prices in different shops and online, you can find
bargains. However, you should think carefully before you buy and decide whether you really need the item.
- Personal budgeting
- you should keep a record of the money you receive, your income, and the money you spend, your expenses.